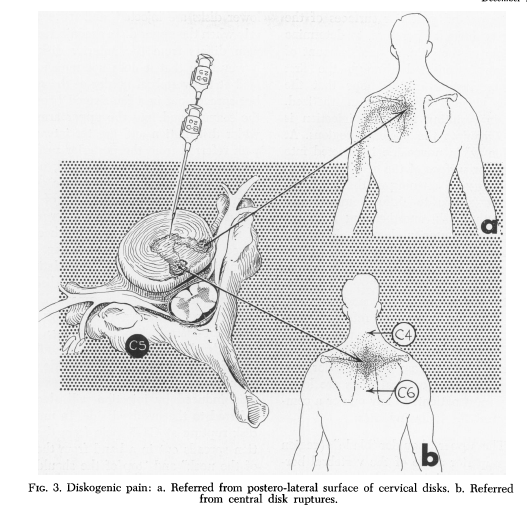
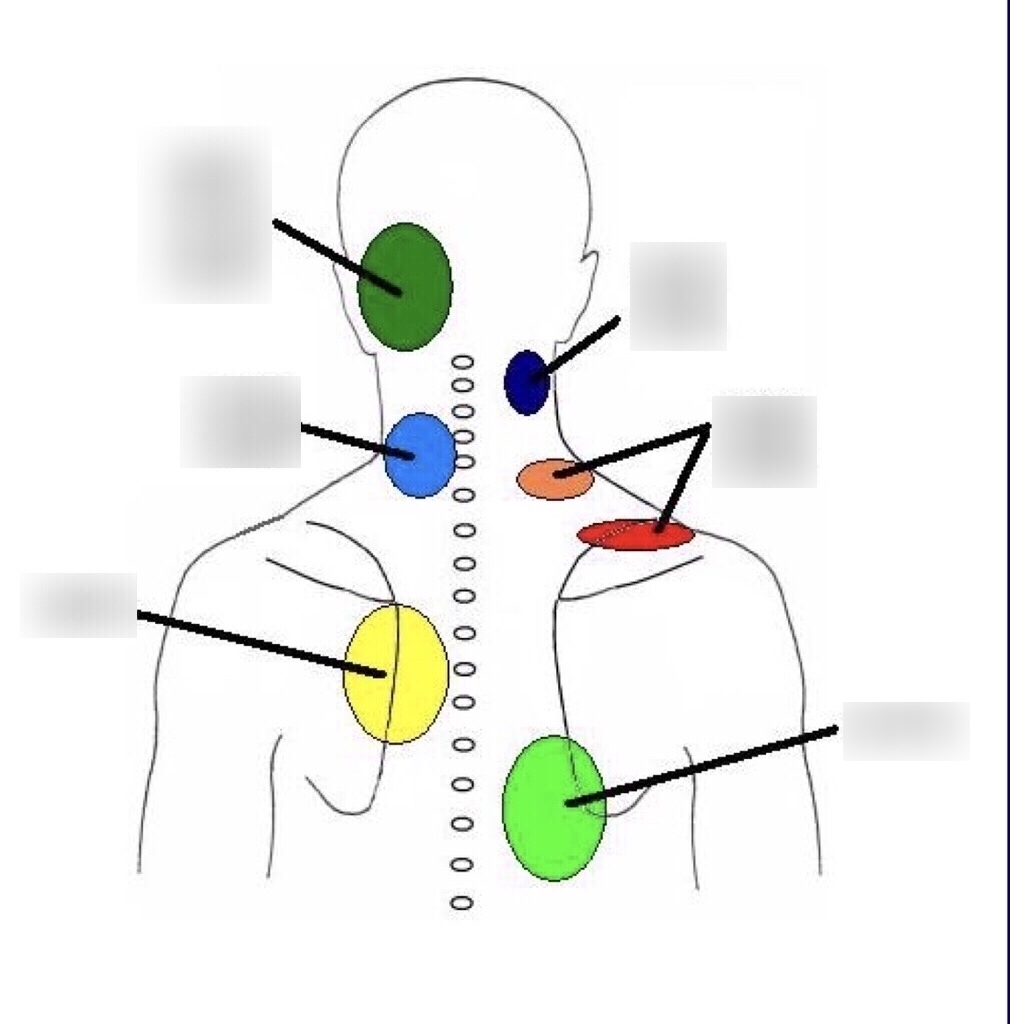
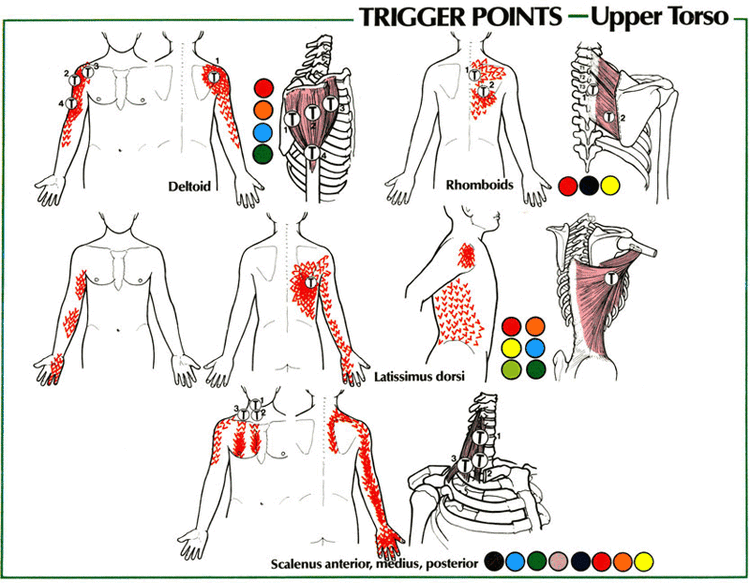
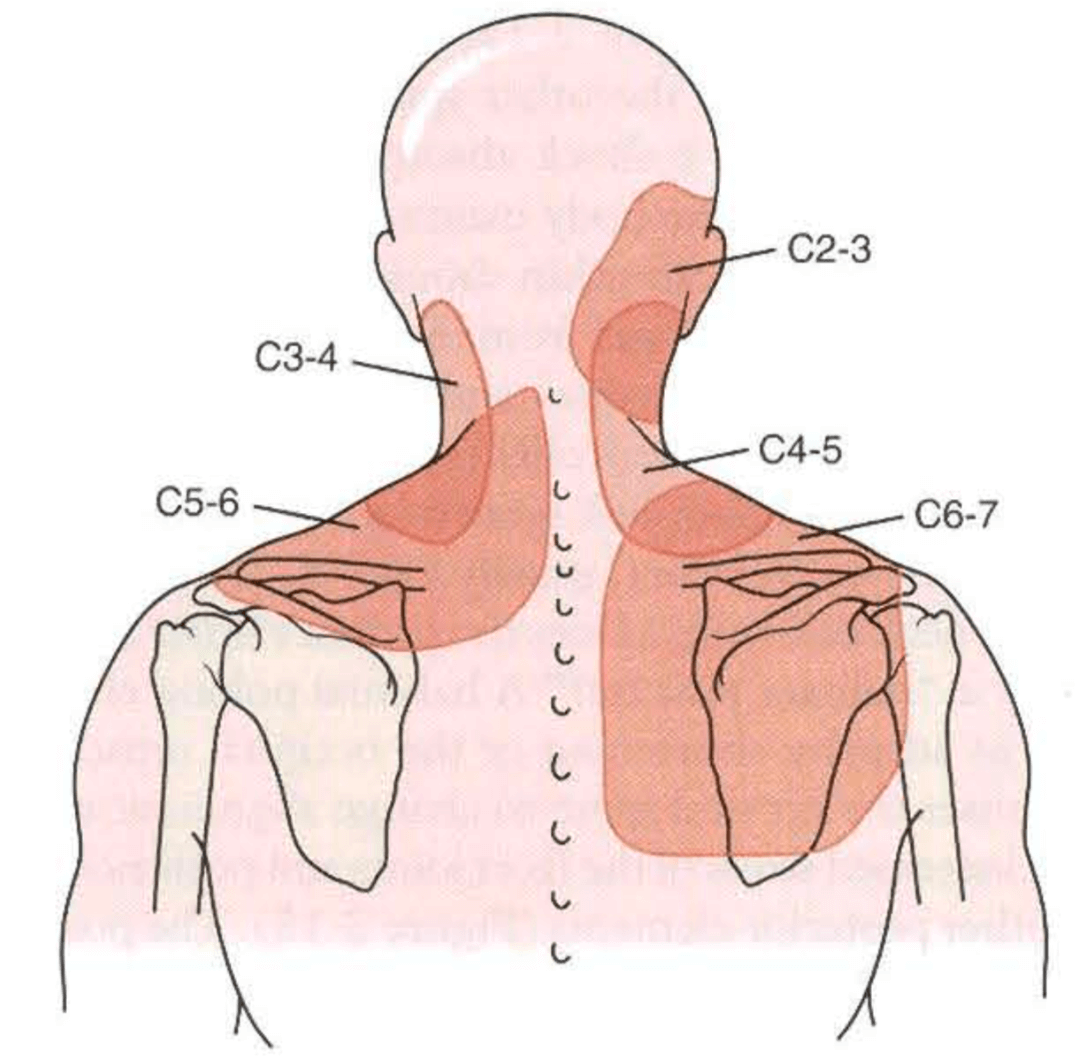
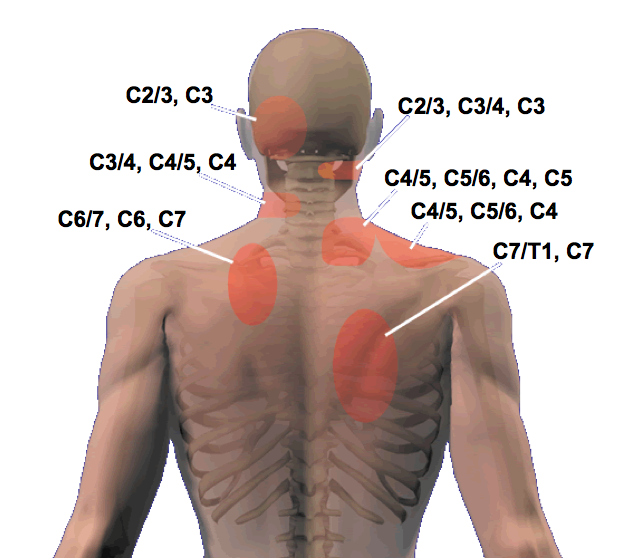
Cervical Referral Patterns
Cervical Referral Patterns - Web cervical facet pain referral patters. Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. Web almost 70% of the global burden falls in areas with lower levels of development. India contributed 28% of cervical cancer mortality burden with 87,090. Web common facet joint disorders are degenerative disorders, such as osteoarthritis, hypertrophied superior articular process, and facet joint cysts; Web disc pain has very similar referral patterns to zygapophyseal joint pain. Web the pain is usually unilateral and radiates in a facet joint referral pattern. [ 32] he found that stimulating the anterolateral. Web a comprehensive recognition of referred pain is important for clinicians when dealing with it. Web cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. Web the pain is usually unilateral and radiates in a facet joint referral pattern. Web the picture below illustrates these patterns (c = cervical vertebrae, t = thoracic vertebrae, number indicates differing spinal level): Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. For example, someone with a c6. Web cervical, thoracic, and lumbar facet joint pain syndromes comprise 55%, 42%, and 31% of chronic spinal pain syndromes, respectively. Web a comprehensive recognition of referred pain is important for clinicians when dealing with it. Web cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. Web in 1959, ralph b. Web cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. Web cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. Web disc pain has very similar referral patterns to zygapophyseal joint pain. [ 32] he found that stimulating the anterolateral. Web a. Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. Pain usually increases with extension ('closing down' of the joint) and reduces with flexion ('opening'. The upper cervical facets are a common source of pain and headache, while pain from the lower cervical facets tends to be felt. The purpose of this study is to summarize the current understanding. Web cervical facet pain referral patters. Web common facet joint disorders are degenerative disorders, such as osteoarthritis, hypertrophied superior articular process, and facet joint cysts; Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. For example, someone with a c6. Web clinical features that are often, but not always, associated with cervical facet pain include tenderness to palpation. Web stimulation of the posterior surface referred to the upper shoulder blade, the base of the neck, the top of the shoulders, the inferior angle of the scapula, and down. Web clinical features that are often, but not always, associated with cervical facet pain include tenderness to palpation over the facet joints or paraspinal muscles, pain with cervical. India contributed. Web learn about the origins and evidence of cervical referral patterns, such as the cloward sign and the bogduk chart, and how to use them in clinical practice. Web clinical features that are often, but not always, associated with cervical facet pain include tenderness to palpation over the facet joints or paraspinal muscles, pain with cervical. Below is the pattern. For example, someone with a c6. Web stimulation of the posterior surface referred to the upper shoulder blade, the base of the neck, the top of the shoulders, the inferior angle of the scapula, and down. Web clinical features that are often, but not always, associated with cervical facet pain include tenderness to palpation over the facet joints or paraspinal. Web in 1959, ralph b. The purpose of this study is to summarize the current understanding of. Web the picture below illustrates these patterns (c = cervical vertebrae, t = thoracic vertebrae, number indicates differing spinal level): India contributed 28% of cervical cancer mortality burden with 87,090. Web common facet joint disorders are degenerative disorders, such as osteoarthritis, hypertrophied superior. Web a comprehensive recognition of referred pain is important for clinicians when dealing with it. Web almost 70% of the global burden falls in areas with lower levels of development. The examination of screening practices. Web common facet joint disorders are degenerative disorders, such as osteoarthritis, hypertrophied superior articular process, and facet joint cysts; Web the picture below illustrates these. Web almost 70% of the global burden falls in areas with lower levels of development. Web cervical, thoracic, and lumbar facet joint pain syndromes comprise 55%, 42%, and 31% of chronic spinal pain syndromes, respectively. Web stimulation of the posterior surface referred to the upper shoulder blade, the base of the neck, the top of the shoulders, the inferior angle. India contributed 28% of cervical cancer mortality burden with 87,090. Web cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. This impingement typically produces neck and. Web clinical features that are often, but not always, associated with cervical facet pain include tenderness to palpation over the facet joints or paraspinal muscles,. The examination of screening practices. Pain usually increases with extension ('closing down' of the joint) and reduces with flexion ('opening'. Web common facet joint disorders are degenerative disorders, such as osteoarthritis, hypertrophied superior articular process, and facet joint cysts; Web cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. Web the picture below illustrates these patterns (c = cervical vertebrae, t = thoracic vertebrae, number indicates differing spinal level): Web cervical, thoracic, and lumbar facet joint pain syndromes comprise 55%, 42%, and 31% of chronic spinal pain syndromes, respectively. Web learn about the origins and evidence of cervical referral patterns, such as the cloward sign and the bogduk chart, and how to use them in clinical practice. Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. Web cervical facet pain referral patters. India contributed 28% of cervical cancer mortality burden with 87,090. Web the pain is usually unilateral and radiates in a facet joint referral pattern. This impingement typically produces neck and. The upper cervical facets are a common source of pain and headache, while pain from the lower cervical facets tends to be felt. Web stimulation of the posterior surface referred to the upper shoulder blade, the base of the neck, the top of the shoulders, the inferior angle of the scapula, and down. Web a comprehensive recognition of referred pain is important for clinicians when dealing with it. The purpose of this study is to summarize the current understanding of.The Cloward Sign...cervical referral patterns — Rayner & Smale
Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine
Cervical Facet Joint Referral Patterns Diagram Quizlet
Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog
Cervical Disc Pain Referral Patterns
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog
Neck pain treatment Manor Chiropractic
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog
Web Referral Patterns For Pain Arising From Ao And Aa Joints.
[ 32] He Found That Stimulating The Anterolateral.
Web Disc Pain Has Very Similar Referral Patterns To Zygapophyseal Joint Pain.
For Example, Someone With A C6.
Related Post: