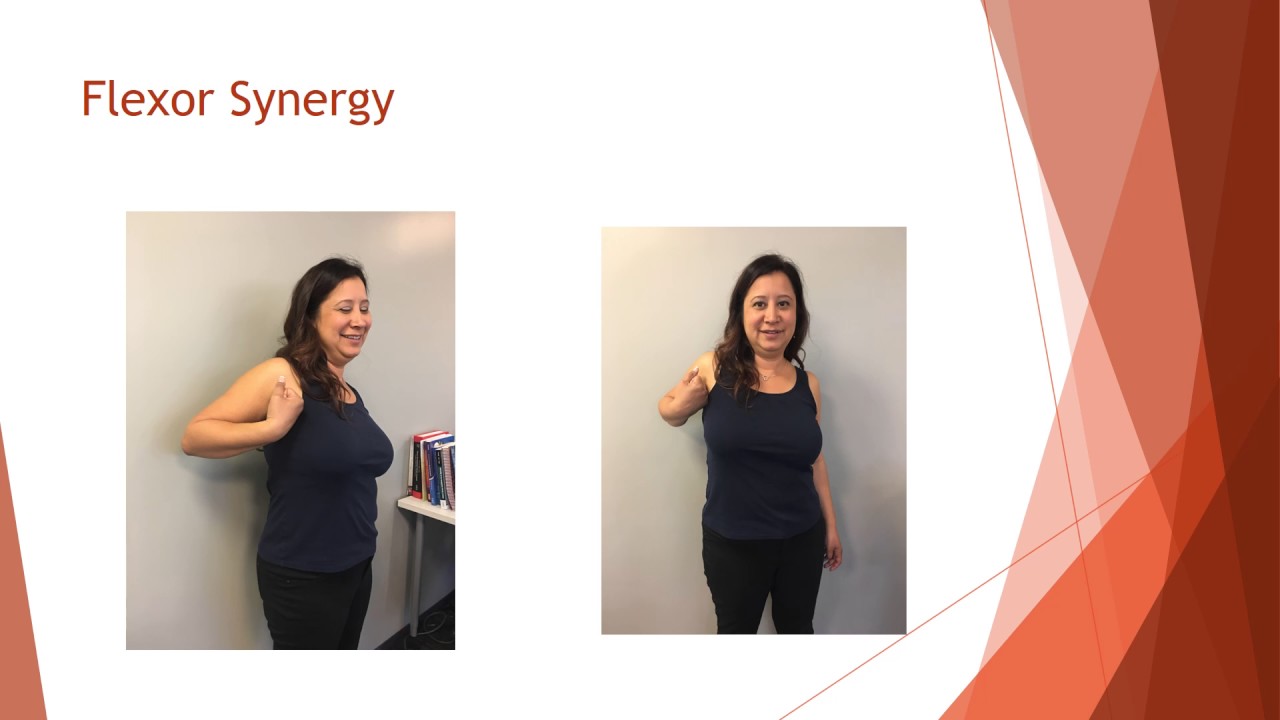
Flexion Synergy Pattern
Flexion Synergy Pattern - Web historically, two main synergies of the upper limb have been identified after stroke. Here you will learn why this happens and. The synergistic movements can be elicited voluntarily but are not obligatory. These are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are obligatorily linked, and the opposite extensor synergy (twitchell, 1951; Movement combining antagonistic synergies can be performed when the prime movers are the strong components of the synergy. Web patients exhibit only few stereotypic movement patterns: Web individuals with this uncontrolled flexion synergy have great difficulty isolating joint movements out of synergy. Web for the lower limb, abnormal synergy is grouped into extension synergy (internal rotation, adduction, and extension of the hip; Synergy patterns can be reversed if movement takes place in. Although this can be a sign of improving communication between your brain and muscles, flexor synergies can be uncomfortable and can lead to complications if not addressed. Web background synergy is an outcome of multiple muscles acting in a synchronized pattern, controlled by the central nervous system. And extension and inversion of the ankle) and flexion synergy (external rotation, abduction, and flexion of the hip; Web synergies consist of stereotypical flexor and extensor movements. The flexor and the extensor synergies. Many patients wonder if they will ever fully recover their muscle coordination, or how long or difficult the process of recovery may be. This reaction is called homolateral synkinesis. Web life after a stroke can be challenging. Shoulder adduction (reaching inward) elbow extension; Web flexor synergy, otherwise known as spasticity, refers to the muscle “drawing” or “pulling in”, in turn making the muscle in a limb feel stiff, tight, or immovable. Web patients exhibit only few stereotypic movement patterns: Web flexor synergy patterns are common after stroke and cause multiple muscle groups to fire at once. Web life after a stroke can be challenging. This reaction is called homolateral synkinesis. These are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are obligatorily linked, and the opposite extensor synergy (twitchell, 1951; Web background synergy is an outcome of. Web life after a stroke can be challenging. The extensor synergy of the arm involves many of the opposite movements, including: Supination (palm facing upwards) wrist and finger flexion; The methods to train synchronization of muscles may diminish the deviated movement augmenting. Web flexor synergy, otherwise known as spasticity, refers to the muscle “drawing” or “pulling in”, in turn making. Shoulder abduction (raising the arm to the side) elbow flexion; Web synergies consist of stereotypical flexor and extensor movements. Based on observations of recovery following a stroke, this approach makes use of associated reactions, tonic reflexes and the development of basic limb synergies to facilitate movements. Many patients wonder if they will ever fully recover their muscle coordination, or how. Web flexion synergy patterns are your brain’s approach to reinforcing muscular control. The synergistic movements can be elicited voluntarily but are not obligatory. 5 spasticity wanes but is evident with rapid movement and at the extremes of range. Web in a classic report, twitchell described in detail the pattern of motor recovery following stroke. By using only a few synergies,. Use of such procedure is temporary. The most common areas affected by flexor synergy are elbow flexion paired with shoulder internal rotation, forearm supination, and grasp. Web synergy patterns can be reversed if movement takes place in the weaker synergy first. These patterns are characterized by involuntary movements such as flexion of the elbow, wrist, and fingers, as well as. The most common areas affected by flexor synergy are elbow flexion paired with shoulder internal rotation, forearm supination, and grasp. Web flexor movement or tone may be elicited in involved arm when the patient attempts to flex the leg or leg flexion is resisted. Supination (palm facing upwards) wrist and finger flexion; Web by applying this gaussian function to express. Synergy patterns can be reversed if movement takes place in. Web for the upper extremity, these stereotyped movement patterns are often described as the flexion synergy (characterized by simultaneous shoulder abduction and elbow flexion) and the extension synergy (characterized by simultaneous shoulder adduction and elbow extension) (trombly and radomski 2002). Shoulder abduction (raising the arm to the side) elbow flexion;. Web patients exhibit only few stereotypic movement patterns: Use of such procedure is temporary. Shoulder abduction (raising the arm to the side) elbow flexion; Web flexor synergy patterns are common after stroke and cause multiple muscle groups to fire at once. Supination (palm facing upwards) wrist and finger flexion; Web flexor movement or tone may be elicited in involved arm when the patient attempts to flex the leg or leg flexion is resisted. At onset, the upper extremity (ue) is more involved than the lower extremity (le), and. Web for the upper extremity, these stereotyped movement patterns are often described as the flexion synergy (characterized by simultaneous shoulder abduction. Managing flexion synergy patterns following a stroke. These patterns are characterized by involuntary movements such as flexion of the elbow, wrist, and fingers, as well as hip and knee flexion. The reconstructed and the recorded patterns of the hand gestures under the test data were then mapped into mitra. Web the third “shoulder adductor/flexor (s add/flex)” synergy was dominated by. And extension and inversion of the ankle) and flexion synergy (external rotation, abduction, and flexion of the hip; Movement combining antagonistic synergies can be performed when the prime movers are the strong components of the synergy. Web flexor synergy patterns are common after stroke and cause multiple muscle groups to fire at once. By using only a few synergies, hand gestures grouped under the testing tasks were reconstructed in the offline model. Web in the arms, flexor synergy refers to: The most common areas affected by flexor synergy are elbow flexion paired with shoulder internal rotation, forearm supination, and grasp. Web synergy patterns can be reversed if movement takes place in the weaker synergy first. Synergy patterns can be reversed if movement takes place in. Web mass synergy patterns (i.e., posturing of limbs and trunk in certain patterns, such as flexion of the upper limb and extension of the lower limb in a stroke patient) Use of such procedure is temporary. This is a lengthy process, but it is feasible to speed it up. The synergistic movements can be elicited voluntarily but are not obligatory. Web for the upper extremity, these stereotyped movement patterns are often described as the flexion synergy (characterized by simultaneous shoulder abduction and elbow flexion) and the extension synergy (characterized by simultaneous shoulder adduction and elbow extension) (trombly and radomski 2002). Web flexor synergy patterns typically involve a coordinated activation of muscles that flex or bend joints, often observed in conditions such as stroke or spinal cord injury. Web the third “shoulder adductor/flexor (s add/flex)” synergy was dominated by activation of bi (a shoulder flexor), ad, md, and pect clav. Web for the lower limb, abnormal synergy is grouped into extension synergy (internal rotation, adduction, and extension of the hip;Flexion synergy pattern after stroke klopnexus
Flexion synergy/ flexor synergy pattern/ flexor synergy pattern upper
Frontiers The Upper Extremity Flexion Synergy Is Minimally Expressed
Flexor Synergy, Spasticity, and Stroke
Flexion Synergy Patterns After Stroke What Are They?
Typical Synergy Patterns Adult and pediatric printable resources for
Flexor Synergy Pattern Upper Extremity Pattern.rjuuc.edu.np
Synergy pattern in 2022 Physical therapy school, Board exam, Finger
Flexion And Upper Limb Spasticity Stroke
Brunnstrom Stages
Although This Can Be A Sign Of Improving Communication Between Your Brain And Muscles, Flexor Synergies Can Be Uncomfortable And Can Lead To Complications If Not Addressed.
Based On Observations Of Recovery Following A Stroke, This Approach Makes Use Of Associated Reactions, Tonic Reflexes And The Development Of Basic Limb Synergies To Facilitate Movements.
Here You Will Learn Why This Happens And.
After Brain Insult, A Set Of Deviated Movement Pattern Emerges In The Affected Limb.
Related Post: